When you admire the sleek lines of a new car door or the robust strength of its chassis, you’re not just looking at steel. You’re witnessing the masterpiece of one of manufacturing’s most critical, yet often overlooked, processes: automotive steel stamping. And at the heart of this high-precision dance are the unsung heroes—the stamping tools and dies.
These aren’t simple hammers and anvils. Automotive stamping tools are complex, custom-engineered marvels that transform flat sheets of steel into the structural bones and beautiful skin of every vehicle on the road. Understanding their role is key to appreciating the modern automotive industry’s scale, precision, and innovation.
More Than Just Metal Bending: The Stamping Process Explained
Automotive steel stamping is a cold-forming process. A massive press, wielding immense force—often hundreds or thousands of tons—drives a tool (the punch) into a sheet of steel against another tool (the die). This action cleanly shears and forms the metal into a specific, pre-determined shape. This single part is known as a stamping.
However, a car is made of thousands of these parts. Doors, hoods, fenders, roof panels, and structural components like frame rails and bumper beams all start their life this way. The process is incredibly fast, cost-effective for high-volume production, and delivers the exceptional strength-to-weight ratio crucial for modern vehicle safety and fuel efficiency.
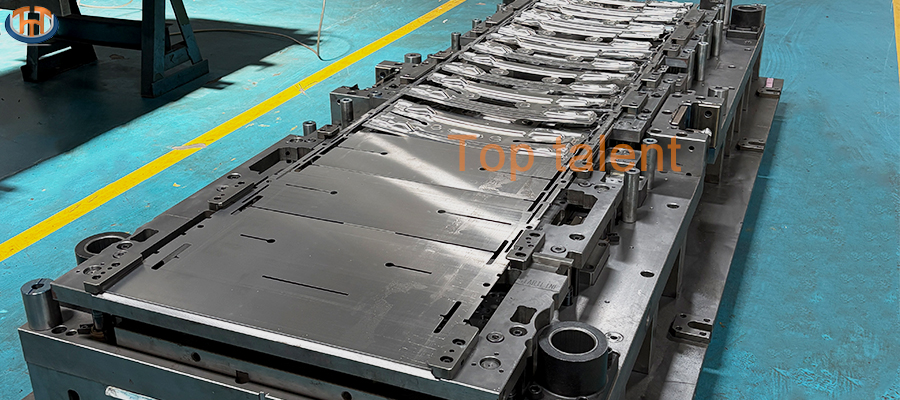
The Anatomy of Precision: What Makes a Stamping Tool?
The terms “stamping tool,” “die,” and “mold” are often used interchangeably, but they refer to the master craftsmen of the production line. These are typically massive blocks of ultra-hardened tool steel, meticulously machined to tolerances finer than a human hair.
Design & Engineering: It all begins with a 3D digital model of the final car part. Toolmakers use sophisticated CAD/CAM software to design the tool’s geometry, accounting for the spring-back of the metal and the complex flow of material during the stamping process.
Manufacturing & Machining: Using CNC mills, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and precision grinding, the tool steel is carved into its final form. This stage requires the skill of master toolmakers, as any flaw in the tool will be replicated on every single part it produces.
Durability & Maintenance: Given the abrasive nature of high-volume stamping, these tools are built to last but require regular maintenance. They are often coated with specialized materials like titanium nitride to reduce wear and extend their lifespan, which can be millions of cycles.
Progressive Stamping: The Pinnacle of Efficiency
For complex parts, a single press stroke isn’t enough. This is where progressive stamping dies shine. A single, intricate tool contains multiple stations. As a long strip of steel feeds through the press, each station performs a different operation—piercing holes, bending flanges, drawing forms—until a finished part is ejected at the end of the cycle. This method is a symphony of mechanical engineering, allowing for the high-speed production of complex components like engine brackets or seat frames.
The Future is Stamped: Innovation in Tooling
The industry is far from static. As automakers push for lighter vehicles and more complex designs, stamping tool technology evolves.
Lightweight Materials: Toolmakers are adapting to work with advanced high-strength steels (AHSS) and aluminum, which behave differently from traditional mild steel and require even more precise tooling.
Digital Twins: Manufacturers now create virtual “digital twins” of their stamping tools. This allows them to simulate the entire stamping process, identifying potential issues like tearing or wrinkling before a single pound of steel is cut, saving immense time and cost.
Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing is used to create conformal cooling channels within the tools themselves, ensuring even temperature distribution and reducing thermal stress during high-speed production.
In conclusion, the next time you see a car, look beyond the paint and chrome. See the seamless body panels, the uniform gaps, and the solid feel. These are the direct results of the precision, durability, and engineering brilliance embedded in automotive steel stamping tools. They are the fundamental, if invisible, foundation upon which the entire industry is built.
Post time: Oct-10-2025


.png)
.png)